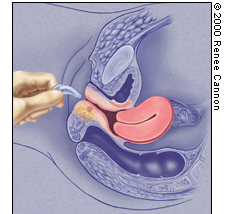
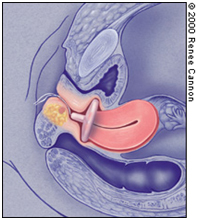
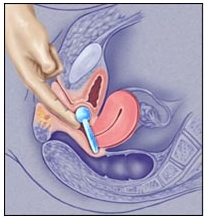
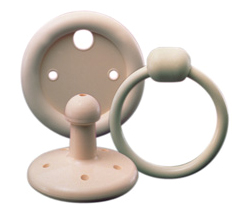
Vaginal Pessaries
Success: About half of the women who are successfully fitted with a pessary will continue to use it on a long-term basis. Typical incontinence pessary users are women who
- Need temporary help with urine leakage during exercise
- Have mild symptoms and want to avoid surgery for the moment
- Have health problems that make the risks of surgery too great
- Need to delay surgery and are uncomfortable from their incontinence
Contraindications to using a pessary:
- vaginal scarring
- surgically narrowed or shortened vagina
- very weak pelvic floor muscles
Pessaries do require ongoing care to avoid problems with vaginal infection, ulceration or bleeding. A neglected pessary can result in erosions through the vaginal wall into the bladder or rectum.
Because incontinence pessaries often apply some pressure on the urethra to prevent urine leakage, ideally a woman is taught to remove, clean and reinsert her pessary on a regular basis. Frequently, vaginal estrogen cream, tablets or a ring are prescribed to women who use a pessary to strengthen the vaginal skin, especially for those in menopause. This will reduce the risk of developing a vaginal skin erosion or ulceration.